SQL catalog reporting and querying: Difference between revisions
m mention RKWeb |
|||
| (2 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
</ul> | </ul> | ||
As an Application Subsystem utility, CCACATREPT is subject to typical Application Subsystem security, as described in [[System requirements for Application Subsystems]]. This is the case whether you are accessing CCACATREPT directly from your Model 204 command line as described on this page, or whether you are accessing from the [[RKWeb]] interface. RKWeb uses [[Janus Web Legacy Support]] to serve facsimiles of the screens described on this page. | As an Application Subsystem utility, CCACATREPT is subject to typical Application Subsystem security, as described in [[System requirements for Application Subsystems]]. This is the case whether you are accessing CCACATREPT directly from your Model 204 command line as described on this page, or whether you are accessing from the [[RKTools#mainmenu|RKTools main menu]] or the [[RKWeb]] interface. RKWeb uses [[Janus Web Legacy Support]] to serve facsimiles of the screens described on this page. | ||
===Logging in=== | ===Logging in=== | ||
Before you can log in to CCACATREPT, the CCACATREPT subsystem must already have been started with the Model 204 <var>START SUBSYSTEM</var> command. If you access CCACATREPT from the RKWeb interface, this command is probably already issued as part of the | Before you can log in to CCACATREPT, the CCACATREPT subsystem must already have been started with the Model 204 <var>START SUBSYSTEM</var> command. If you access CCACATREPT from the RKWeb interface, this command is probably already issued as part of the [[RKTools installation#Janus Web rules for RKWeb|recommended set up for RKWeb]]. | ||
To log in to CCACATREPT, at your Model 204 Online prompt enter <code><b>CCACATREPT</b></code> and press Enter. | To log in to CCACATREPT, at your Model 204 Online prompt enter <code><b>CCACATREPT</b></code> and press Enter. | ||
The CCACATREPT Main Menu is displayed. | The CCACATREPT Main Menu is displayed. | ||
| Line 153: | Line 153: | ||
The first reporting option on the Main Menu is to generate the SQL DDL from the existing SQL catalog (CCACAT file) data. This DDL is output in valid SQL syntax that you can use to rebuild the catalog. You can also use it to report the existing catalog data in a standard format familiar to SQL users.</p> | The first reporting option on the Main Menu is to generate the SQL DDL from the existing SQL catalog (CCACAT file) data. This DDL is output in valid SQL syntax that you can use to rebuild the catalog. You can also use it to report the existing catalog data in a standard format familiar to SQL users.</p> | ||
<p class="note"><b>Note:</b> Currently the CCACATREPT subsystem does not generate DDL statement delimiters. However, semicolons are required by the CVI utility. You can add delimiters by hand or use another SQL utility that does not require DDL delimiters. The Connect<span class="superstar">★</span> ODBC unsupported utilities, DDLWIN and CLIIVP, are examples of utilities which accept DDL input lines without delimiters.</p> | <p class="note"><b>Note:</b> Currently the CCACATREPT subsystem does not generate DDL statement delimiters. However, semicolons are required by the CVI utility. You can add delimiters by hand or use another SQL utility that does not require DDL delimiters. The [[Connect*_for_ODBC|Connect<span class="superstar">★</span> for ODBC]] unsupported utilities, DDLWIN and CLIIVP, are examples of utilities which accept DDL input lines without delimiters.</p> | ||
===Specifying report input parameters=== | ===Specifying report input parameters=== | ||
Latest revision as of 19:09, 27 October 2017
To review the current contents of the SQL catalog you can query the catalog directly or you can use CCACATREPT, the SQL catalog reporting utility. This topic describes CCACATREPT and the queriable views of the SQL catalog.
SQL catalog reporting with CCACATREPT
The CCACATREPT subsystem is a reporting mechanism for data in the CCACAT SQL catalog file. CCACATREPT is a menu-driven utility that produces both online and printed output. With CCACATREPT you can produce a report that provides information about all SQL objects defined in the SQL catalog.
Catalog administrators can compare the CCACATREPT output to the Model 204 file data to determine the updates they need to make to the SQL catalog to obtain consistency with the file. They can modify the report's generated DDL and use it to repopulate the SQL catalog. SQL application programmers and SQL users can use the output to verify valid table, view, column names and column attributes.
This section describes the CCACATREPT menu and provides examples of each of the output formats. CCACATREPT produces the following types of online and printed output:
- File of valid DDL syntax, which you can use to rebuild the catalog
- Fixed format report of a table or view
- Privilege report by table or view name
- Privilege report by user
As an Application Subsystem utility, CCACATREPT is subject to typical Application Subsystem security, as described in System requirements for Application Subsystems. This is the case whether you are accessing CCACATREPT directly from your Model 204 command line as described on this page, or whether you are accessing from the RKTools main menu or the RKWeb interface. RKWeb uses Janus Web Legacy Support to serve facsimiles of the screens described on this page.
Logging in
Before you can log in to CCACATREPT, the CCACATREPT subsystem must already have been started with the Model 204 START SUBSYSTEM command. If you access CCACATREPT from the RKWeb interface, this command is probably already issued as part of the recommended set up for RKWeb.
To log in to CCACATREPT, at your Model 204 Online prompt enter CCACATREPT and press Enter.
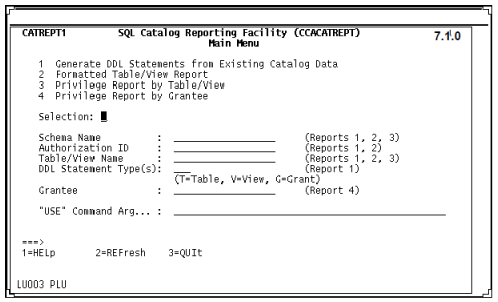
The CCACATREPT Main Menu is displayed.
CCACATREPT Main Menu
The Main Menu of CCACATREPT in the following figure displays the four output formats, their input parameters, and their output destination options.
CCACATREPT Main Menu
Using the CCACATREPT panel
After you make final panel field selections and generate a report, CCACATREPT redisplays the panel with those selections.
You can enter an asterisk (*) in an input area to select all the items of a particular category.
The command line (===>) is at the bottom of the panel. Use the command line to enter commands in lieu of PF keys. The minimum abbreviation for a command is generally the first three characters, for example, REF for REFresh. The minimum abbreviation appears in capital letters in the PF key display area.
The PF keys of the CCACATREPT main menu are described in the following table. In the RKWeb display, comparable buttons replace the PF keys.
CCACATREPT main menu PF keys
| Key | Explanation |
|---|---|
| PF1 = HELp |
You can access either general help information for the panel or additional individual panel field help information. To access general help information for this panel: To access individual panel field help information: |
| PF2 = REFresh |
Refresh the screen, and do not process the current data on the screen. The refreshed screen appears as it does when you first entered the panel. |
| PF3 = QUIt | Exit from CCACATREPT. Entries are not saved when you use PF3. |
Selection field
Using the Selection field you can generate output from any of the four reports numbered one through four on the menu. Enter an integer from 1 through 4, corresponding to the reports numbered on the menu. The report number you choose determines the input parameter fields. Your must supply one of the values that are listed below the Selection field. The report input parameter fields are followed by a specification in parentheses of the reports for which a value is required.
If you supply a value for a report that does not require it, you receive an error message asking you to remove your incorrect value.
Schema Name field
You must specify an entry in this field if you entered 1, 2, or 3 in the Selection field. Enter the name of a specific schema or enter an asterisk (*) for all schemas.
If your Selection field entry requires an entry for this field and you do not enter a value, by default CCACATREPT outputs all schemas.
Authorization ID field
You must specify an entry in this field if you entered 1 or 2 in the Selection field. Enter the name of a specific authorization ID or enter an asterisk (*) for all authorization IDs.
If your Selection field entry requires an entry for this field and you do not enter a value, by default CCACATREPT outputs all authorization IDs.
Table/View Name field
You must specify an entry in this field if you entered 1, 2, or 3 in the Selection field. Enter the name of a specific table or view to be reported or enter an asterisk (*) for all tables and views.
If your Selection field entry requires an entry for this field and you do not enter a value, by default CCACATREPT outputs all tables and views.
DDL Statement Type(s) field
You must specify an entry in this field if you entered 1 in the Selection field. The output from Selection 1 is standard SQL DDL generated from the Model 204 SQL catalog. In the DDL Statement Type(s) field, you identify the DDL statement types to be generated.
Select one or more of the following identifiers:
| Identifier | Statement generated |
|---|---|
| T | CREATE TABLE |
| V | CREATE VIEW |
| G | GRANT |
| T, V, or G | CREATE SCHEMA or SET SCHEMA CREATE TABLE, CREATE VIEW, and GRANT |
If your Selection field entry requires an entry for this field and you do not enter a value, by default CCACATREPT outputs all the DDL.
Grantee field
You must specify an entry in this field if you entered 4 in the Selection field. Enter the SQL identifier of a specific grantee to be reported or enter an asterisk (*) for all grantees. Privileges granted to PUBLIC are always reported.
If your Selection field entry requires an entry for this field and you do not enter a value, by default CCACATREPT outputs privileges for all grantees.
"USE" Command Arg
Use this field to route output to a destination other than to the terminal. The character string you enter in this field becomes the Model 204 USE command argument that identifies the output destination device.
You can enter any USE command argument that is valid in your operating environment, for example, PRINTER FOO or $PRINT *.
You can route your output to a file. Either dynamically allocate or have your system manager define or allocate an output file prior to your using it from CCACATREPT. For best results under z/OS (and comparably for VM and VSE), make sure that the following are specified in the DD statement or ALLOCATE command for the output file (data set):
- DD name begins with OUT.
- DISP=MOD, if you intend to generate multiple reports before processing the output file
- RECFM=FS, to prevent the printing to the file of carriage control characters
- LRECL=80, to facilitate the reading of the file by CVI or other DDL utility
For more information about the USE command, see USE command: Directing output.
Report Selection 1: Generate DDL
The first reporting option on the Main Menu is to generate the SQL DDL from the existing SQL catalog (CCACAT file) data. This DDL is output in valid SQL syntax that you can use to rebuild the catalog. You can also use it to report the existing catalog data in a standard format familiar to SQL users.
Note: Currently the CCACATREPT subsystem does not generate DDL statement delimiters. However, semicolons are required by the CVI utility. You can add delimiters by hand or use another SQL utility that does not require DDL delimiters. The Connect★ for ODBC unsupported utilities, DDLWIN and CLIIVP, are examples of utilities which accept DDL input lines without delimiters.
Specifying report input parameters
The required input parameters are described in the following table.
| Required parameter | Enter... |
|---|---|
| Schema Name | Specific name, or asterisk (*) |
| Authorization ID | Specific ID, or asterisk (*) |
| Table/View Name | Specific name, or asterisk (*) |
| DDL Statement Types | String of identifiers for the DDL statement types to be generated.
Enter one or more of the following options, without commas or spaces: |
Report input parameter examples
The following examples describe how the report input parameters are used.
Example 1
Specifying the parameters in this example produces CREATE SCHEMA, CREATE TABLE, CREATE VIEW, and GRANT DDL statements for all CCACAT objects.
Schema Name = * Authorization ID = * Table/View Name = * DDL Statement Types = tvg
Example 2
Specifying the parameters in this example produces SET SCHEMA and CREATE TABLE DDL statements for all tables with the authorization ID of USERxxx.
Schema Name = * Authorization ID = userxxx Table/View Name = * DDL Statement Types = t
Example 3
Specifying the parameters in this example produces SET SCHEMA, CREATE TABLE, and GRANT DDL statements for the table USERxxx.CLIENTS.
Schema Name = * Authorization ID = userxxx Table/View Name = clients DDL Statement Types = tg
Ordering the DDL output
The format of the DDL generated by this report option is the same as that generated by the TSF.
To set the schema context, CCACATREPT always places the CREATE SCHEMA or SET SCHEMA statement before the rest of the generated DDL. If you plan to process the generated DDL against the SQL catalog, you might have to change CREATE SCHEMA to SET SCHEMA, because issuing CREATE SCHEMA for a schema that already exists is an error.
For more information about creating schemas, changing the default schema context, and SQL DDL statement processing, see Setting the schema and user context.
You must order statements correctly to avoid forward referencing problems when the generated DDL is processed. For example, a view of a view must reference an already created view. The generated DDL sort order follows:
- Schemas in the order that they were originally input into the SQL catalog.
- Within a schema, all base and parent tables in alphanumeric order, followed by all nested tables in alphanumeric order. Privileges (GRANT statements) for each table follow that table.
- Views follow tables. They are in the order that they were originally input into the SQL catalog. GRANT statements for each view follow that view.
- Grants are ordered by privilege, column name, GRANT statement option, and grantee.
Sample of generated DDL
The sample DDL stream in the following figure is generated by the following input parameter specifications:
Schema Name = demo Authorization ID = * Table/View Name = clients DDL Statement Types = tvg
Sample DDL output
SET SCHEMA DEMO CREATE TABLE CLIENTS ( ADDRESS CHAR(40), AGENT CHAR(20), ANNIV_DATE SYSNAME 'ANNIV DATE' INT, CITY CHAR(20), DATE_OF_BIRTH SYSNAME 'DATE OF BIRTH' INT, DRIVER_ID SYSNAME 'DRIVER ID' INT, FULLNAME CHAR(40) NOT NULL, MARITAL_STATUS SYSNAME 'MARITAL STATUS' CHAR(15), POLICY_NO SYSNAME 'POLICY NO' CHAR(6) NOT NULL, POLICYHOLDER CHAR(40), RECTYPE CHAR(15) NOT NULL, RESTRICTIONS CHAR(255), SEX CHAR(1), STATE CHAR(25), TOTAL_PREMIUM SYSNAME 'TOTAL PREMIUM' INT, ZIP CHAR(9), PID INT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY SYSTEM) -- GRANT STATEMENTS FOR TABLE: CLIENTS GRANT DELETE ON CLIENTS TO PUBLIC GRANT INSERT ON CLIENTS TO PUBLIC GRANT SELECT ON CLIENTS TO PUBLIC GRANT UPDATE ON CLIENTS TO PUBLIC
Report Selection 2: Formatted Table/View report
The Formatted Table/View report has a fixed format that provides the same information as the DDL generation report (except for granted privilege information), but in a different format.
Report input parameters
Input parameters for the report are:
- Specific schema name, or asterisk (*)
- Specific authorization ID, or asterisk (*)
- Specific table or view name, or asterisk (*)
Contents of the report
The report provides the following information for tables (see Sample report):
- Name of the SQL table
- Column names in the table
- SQL attributes of table columns
- Column names making up any multi-column unique columns
- Name of the corresponding Model 204 file
- Name of the corresponding Model 204 field
- Authorization ID
Note: The report does not provide information about views that reference a given table.
The report provides the following information for views:
- Name of the SQL view
- View definition text
Sample report
In the following figure, the sample output is generated by the following input parameter specifications:
Schema Name = demo Authorization ID = userxxx Table/View Name = clients
The output is a formatted table/view report of the DEMO.CLIENTS table.
Sample Table/View report
18 NOV 09 SQL SCHEMA, TABLE, VIEW REPORT SCHEMA: DEMO AUTHORIZATION: USERXXX TABLE: CLIENTS TABLE-TYPE: PARENT PRIMARY-KEY: PID M204-FILE: CLIENTS SQL-COLUMN-NAME DATA-TYPE NULL UNQ MODEL-204-FIELD-NAME ADDRESS CHAR(40) Y N ADDRESS AGENT CHAR(20) Y N AGENT ANNIV_DATE INT Y N ANNIV DATE CITY CHAR(20) Y N CITY DATE_OF_BIRTH INT Y N DATE OF BIRTH DRIVER_ID INT Y N DRIVER ID FULLNAME CHAR(40) N N FULLNAME MARITAL_STATUS CHAR(15) Y N MARITAL STATUS POLICY_NO CHAR(6) N N POLICY NO POLICYHOLDER CHAR(40) Y N POLICYHOLDER RECTYPE CHAR(15) N N RECTYPE RESTRICTIONS CHAR(255) Y N RESTRICTIONS SEX CHAR(1) Y N SEX STATE CHAR(25) Y N STATE TOTAL_PREMIUM INT Y N TOTAL PREMIUM ZIP CHAR(9) Y N ZIP PID INT N Y PID
Report Selection 3: Privilege report by table/view
The Privilege report by table/view displays the DML update privileges for each table and view indicated by your input parameter specification. The update operations permitted per table and view, including WITH GRANT OPTION, are displayed for each grantee and for grants to PUBLIC.
The report has a fixed format. The sort order is by object name (schema name and table or view name), within that by grantee, and within that by column name, if applicable.
Report input parameters
Input parameters for the report are:
- Specific schema name, or asterisk (*)
- Specific table or view name, or asterisk (*)
Report display fields
The following table lists the report display fields and their meanings.
Privilege report by table/view display fields
| Field | Meaning |
|---|---|
| TABLE/VIEW | Name of the table or view for which indicated privileges are valid. |
| GRANTEE | User ID for which the privileges are granted. |
| SEL | If X, privilege to issue DML SELECT statement. If blank, no such privilege. |
| INS | If X, privilege to issue DML INSERT statement. If blank, no such privilege. |
| DEL | If X, privilege to issue DML DELETE statement. If blank, no such privilege. |
| UPD | If X, privilege to issue DML UPDATE statement. If blank, no such privilege. |
| OPT | If Y, option to grant this privilege to others. If N, no such privilege. |
| COLUMN-NAME | For UPDATE only, specific columns for which the privilege is granted. Asterisk (*) means all columns. |
Sample Privilege Report by table and view
The sample output in the following figure is generated by the following input parameter specifications:
Schema Name = demo Table/View Name = *
The output is a privilege report for all the tables and views in the DEMO schema.
Sample Privilege Report by table/view
18 NOV 09 SQL PRIVILEGE REPORT -- BY TABLE/VIEW PAGE: 1 TABLE/VIEW: DEMO.ACCIDENTS GRANTEE SEL-OPT INS-OPT DEL-OPT UPD-OPT COLUMN-NAME PUBLIC X N X N X N X N USERXXX X Y X Y X Y X Y TABLE/VIEW: DEMO.CLAIMS03 GRANTEE SEL-OPT INS-OPT DEL-OPT UPD-OPT COLUMN-NAME PUBLIC X N X N X N X N USERXXX X Y X Y X Y X Y TABLE/VIEW: DEMO.CLIENTS GRANTEE SEL-OPT INS-OPT DEL-OPT UPD-OPT COLUMN-NAME PUBLIC X N X N X N X N USERXXX X Y X Y X Y X Y TABLE/VIEW: DEMO.DRIVERS GRANTEE SEL-OPT INS-OPT DEL-OPT UPD-OPT COLUMN-NAME PUBLIC X N X N X N X N USERXXX X N X N X N X Y TABLE/VIEW: DEMO.INSURED_VINS GRANTEE SEL-OPT INS-OPT DEL-OPT UPD-OPT COLUMN-NAME PUBLIC X N X N X N X N USERXXX X Y X Y X Y X Y TABLE/VIEW: DEMO.OTHER_DRIVER GRANTEE SEL-OPT INS-OPT DEL-OPT UPD-OPT COLUMN-NAME PUBLIC X N X N X N X N USERXXX X Y X Y X Y X Y TABLE/VIEW: DEMO.POLICIES GRANTEE SEL-OPT INS-OPT DEL-OPT UPD-OPT COLUMN-NAME PUBLIC X N X N X N X N USERXXX X N X N X N X Y TABLE/VIEW: DEMO.VEHICLES GRANTEE SEL-OPT INS-OPT DEL-OPT UPD-OPT COLUMN-NAME PUBLIC X N X N X N X N USERXXX X Y X Y X Y X Y 18 NOV 09 SQL PRIVILEGE REPORT -- BY TABLE/VIEW PAGE: 2
Report Selection 4: Privilege report by grantee
The Privilege report by grantee displays the DML update privileges for each grantee indicated by your input parameter specification. The update operations permitted, including WITH GRANT OPTION, are displayed for each table or view. Privileges granted to PUBLIC are displayed under GRANTEE=PUBLIC.
The report has a fixed format. The sort order is by grantee, within that by object name (schema name and table or view name), and within that by column name, if applicable.
Report input parameter
The required input parameter for the report is: Specific grantee (or *).
Report display fields
The report display fields have the same meanings as those for Privilege report by table/view display fields.
Sample report
A sample of this report appears in the following figure, generated by the following input parameter specification:
Grantee = userxxx
The output is a report of all the privileges granted to USERXXX or to PUBLIC.
Sample Privilege report by grantee
18 NOV 09 SQL PRIVILEGE REPORT -- BY GRANTEE PAGE: 1 GRANTEE: PUBLIC TABLE/VIEW SEL-OPT INS-OPT DEL-OPT UPD-OPT COLUMN-NAME DEMO.ACCIDENTS X N X N X N X N DEMO.CLAIMS03 X N X N X N X N DEMO.CLIENTS X N X N X N X N DEMO.DRIVERS X N X N X N X N DEMO.INSURED_VINS X N X N X N X N DEMO.OTHER_DRIVER X N X N X N X N DEMO.POLICIES X N X N X N X N DEMO.VEHICLES X N X N X N X N GRANTEE: USERXXX TABLE/VIEW SEL-OPT INS-OPT DEL-OPT UPD-OPT COLUMN-NAME DEMO.ACCIDENTS X Y X Y X Y X Y DEMO.CLAIMS03 X Y X Y X Y X Y DEMO.CLIENTS X Y X Y X Y X Y DEMO.DRIVERS X N X N X N X Y DEMO.INSURED_VINS X Y X Y X Y X Y DEMO.OTHER_DRIVER X Y X Y X Y X Y DEMO.POLICIES X N X N X N X Y DEMO.VEHICLES X Y X Y X Y X Y
Querying the SQL catalog
You can directly query the Model 204 SQL catalog to obtain information about the current catalog definitions. Any authorized SQL user can access (but not update) any of 18 views of the catalog contents. You use a normal SQL query and devise your own report format for information from the catalog views.
The SQL catalog contains a schema named CATALOG that is comprised of the views of the catalog contents. The views are defined by SQL object. For example, the schemas view in CATALOG contains all the schemas in the catalog by name and by authorization ID.
The CATALOG views are listed here and described individually in the rest of this section.
SCHEMAS (or SCHEMATA) TABLES TABLE_COLUMNS COLUMNS (for tables and views) VIEWS TABLE_CONSTRAINTS KEY_COLUMN_USAGE TABLE_PRIVILEGES COLUMN_PRIVILEGES ODBC_TYPES ODBC_SCALES CONST ODBC_COLUMNS ODBC_SPECIAL_COLS ODBC_TABLES ODBC_TABLE_STATS ODBC_KEY_STATS ODBC_STATISTICS
Querying a CATALOG view
Authorized Model 204 SQL users can query any of the CATALOG views like any other SQL object. However, the views display to you only the SQL objects or information that you have the authority to see or that are granted to PUBLIC.
For example, USERXXX issues the following query against the Model 204 demonstration database:
SELECT * FROM CATALOG.TABLES
The result is a display of information about the tables USERXXX has the authority to select or update. The query's output is shown in the following figure. The format of the output depends on your application and is your responsibility.
The CATALOG.TABLES columns (described in TABLES view), ordered from left to right, are:
TABLE_CATALOG, TABLE_SCHEMA, TABLE_NAME, FILE_NAME, TABLE_TYPE, COLUMN_CARDINALITY, PRIMARY_KEY, SYSTEM_KEY, PARENT_TABLE_NAME, TIMESTAMP
This is the default display order, which derives from the order of the columns in the individual CATALOG view definition.
CCACAT |
CATALOG |
SCHEMAS |
|
V |
4 |
|
4 |
|
19920911000004 |
CCACAT |
CATALOG |
TABLES |
|
V |
10 |
|
10 |
|
19920911000007 |
CCACAT |
CATALOG |
TABLE_COLUMNS |
|
V |
11 |
|
11 |
|
19920911000010 |
CCACAT |
CATALOG |
COLUMNS |
|
V |
8 |
|
8 |
|
19920911000000 |
CCACAT |
CATALOG |
VIEWS |
|
V |
6 |
|
6 |
|
19920911000016 |
CCACAT |
CATALOG |
TABLE_CONSTRAINTS |
|
V |
6 |
|
6 |
|
19920911000019 |
CCACAT |
CATALOG |
KEY_COLUMN_USAGE |
|
V |
5 |
|
5 |
|
19920911000022 |
CCACAT |
CATALOG |
TABLE_PRIVILEGES |
|
V |
8 |
|
8 |
|
19920911000025 |
CCACAT |
CATALOG |
COLUMN_PRIVILEGES |
|
V |
9 |
|
9 |
|
19920911000028 |
CCACAT |
CATALOG |
ODBC_TYPES |
|
V |
|
|
16 |
|
19981201142400 |
CCACAT |
CATALOG |
ODBC_SCALES |
|
V |
|
|
2 |
|
19981201142400 |
CCACAT |
CATALOG |
CONST |
|
V |
|
|
9 |
|
19981201142400 |
CCACAT |
CATALOG |
ODBC_COLUMNS |
|
V |
|
|
17 |
|
19981201142400 |
CCACAT |
CATALOG |
ODBC_SPECIAL_COLS |
|
V |
|
|
10 |
|
19981201142400 |
CCACAT |
CATALOG |
ODBC_TABLES |
|
V |
|
|
5 |
|
19981201142401 |
CCACAT |
CATALOG |
ODBC_TABLE_STATS |
|
V |
|
|
12 |
|
19981201142401 |
CCACAT |
CATALOG |
ODBC_KEY_STATS |
|
V |
|
|
12 |
|
19981201142401 |
CCACAT |
CATALOG |
ODBC_STATISTICS |
|
V |
|
|
12 |
|
19981201142401 |
CCACAT |
USERXXX |
DRIVERS |
|
V |
9 |
|
|
|
19921117183249 |
CCACAT |
USERXXX |
POLICIES |
|
V |
9 |
|
|
|
19921117183250 |
CCACAT |
USERXXX |
CLIENTS |
CLIENTS |
T |
17 |
PID |
1 |
|
19921117183251 |
CCACAT |
USERXXX |
ACCIDENTS |
CLIENTS |
T |
3 |
PID |
1 |
CLIENTS |
19921117183253 |
CCACAT |
USERXXX |
INSURED_VINS |
CLIENTS |
T |
2 |
PID |
1 |
CLIENTS |
19921117183254 |
CCACAT |
USERXXX |
VEHICLES |
VEHICLES |
T |
19 |
VIN |
0 |
CLIENTS |
19921117183254 |
CCACAT |
USERXXX |
OTHER_DRIVER |
VEHICLES |
T |
2 |
VIN |
0 |
VEHICLES |
19921117183256 |
CCACAT |
USERXXX |
CLAIMS03 |
CLAIMS03 |
T |
13 |
VIN |
0 |
VEHICLES |
19921117183258 |
The output in the previous figure is from two schemas: CATALOG and USERXXX. The CATALOG schema contains the 18 views that describe the catalog contents and is granted to PUBLIC. You can limit the output to the tables in schema USERXXX by using the following SELECT statement:
SELECT * FROM CATALOG.TABLES WHERE TABLE_SCHEMA='USERXXX'
You can list specific columns for display instead of using SELECT *. For example, the following statement results in the same display as that in the previous figure:
SELECT TABLE_CATALOG, TABLE_SCHEMA, TABLE_NAME, FILE_NAME, TABLE_TYPE, COLUMN_CARDINALITY, PRIMARY_KEY, SYSTEM_KEY, PARENT_TABLE_NAME, TIMESTAMP FROM CATALOG.TABLES
The output in the previous figure is grouped by schema, because that is how the DDL used to populate the SQL catalog was organized. An unqualified SQL catalog query returns data chronologically in the order in which the SQL objects were defined or updated in the SQL catalog. As new tables are added to which USERXXX is granted access, this convenient grouping is likely to be lost.
You can ensure that your output is appropriately ordered by sorting the rows by column value with the ORDER BY clause. For example, the following statement sorts the query output by table name, as shown in the following figure:
SELECT * FROM CATALOG.TABLES WHERE TABLE_SCHEMA='USERXXX' ORDER BY TABLE_SCHEMA, TABLE_NAME
CCACAT |
USERXXX |
ACCIDENTS |
CLIENTS |
T |
3 |
PID |
1 |
CLIENTS |
19921117183253 |
CCACAT |
USERXXX |
CLAIMS03 |
CLAIMS03 |
T |
13 |
VIN |
0 |
VEHICLES |
19921117183258 |
CCACAT |
USERXXX |
CLIENTS |
CLIENTS |
T |
17 |
PID |
1 |
|
19921117183251 |
CCACAT |
USERXXX |
DRIVERS |
|
V |
9 |
|
|
|
19921117183249 |
CCACAT |
USERXXX |
INSURED_VINS |
CLIENTS |
T |
2 |
PID |
1 |
CLIENTS |
19921117183254 |
CCACAT |
USERXXX |
OTHER_DRIVER |
VEHICLES |
T |
2 |
VIN |
0 |
VEHICLES |
19921117183256 |
CCACAT |
USERXXX |
POLICIES |
|
V |
9 |
|
|
|
19921117183250 |
CCACAT |
USERXXX |
VEHICLES |
VEHICLES |
T |
19 |
VIN |
0 |
CLIENTS |
19921117183254 |
Rules for CATALOG queries
- A query against a table that does not exist returns an empty result.
- A query against a table that you do not have the authority to access returns an empty result.
- You cannot issue update SQL DML against the CATALOG views.
SCHEMAS view
The following table lists the CATALOG.SCHEMAS view columns and their descriptions. This view contains a row of identifying information for each schema whose authorization ID is your login ID.
SCHEMATA is an alias for SCHEMAS. You can query either SCHEMAS or SCHEMATA.
The top-to-bottom order of the columns in the following table is the left-to-right order of the columns in each row of output you receive from an unqualified SELECT * query against the view.
| Column name | Data type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| SCHEMA_CATALOG | CHAR(18) | Name of the catalog where the schema is cataloged (CCACAT) |
| SCHEMA_NAME | CHAR(18) | Name of the schema |
| SCHEMA_OWNER | CHAR(18) | Authorization ID of the owner of the schema |
| TIMESTAMP | CHAR(14) | Greenwich mean time when the schema description was cataloged |
TABLES view
The following table lists the CATALOG.TABLES view columns and their descriptions. This view contains a row of descriptive information for each table or view you have the authority to access.
The top-to-bottom order of the columns in the following table is the left-to-right order of the columns in each row of output you receive from an unqualified SELECT * query against the view.
| Column name | Data type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| TABLE_CATALOG | CHAR(18) | Name of the catalog in which the table is cataloged (CCACAT) |
| TABLE_SCHEMA | CHAR(18) | Name of the schema to which the table belongs |
| TABLE_NAME | CHAR(18) | Name of the table |
| FILE_NAME | CHAR(8) | Name of the Model 204 file to which the table maps |
| TABLE_TYPE | CHAR(1) | Type of table: either T (table), or V (view) |
| COLUMN_CARDINALITY | INTEGER | Number of columns defined in the table being described |
| PRIMARY_KEY | CHAR(18) | Name of any primary or nested key column; otherwise, null |
| SYSTEM_KEY | CHAR(1) | 0 if the primary or nested key column is not system-generated 1 if the primary or nested key column is system-generated null if there is no primary or nested key |
| PARENT_TABLE_NAME | CHAR(18) | Name of parent table if the table is nested; otherwise, null |
| TIMESTAMP | CHAR(14) | Greenwich mean time when the table description was cataloged |
TABLE_COLUMNS view
The following table lists the CATALOG.TABLE_COLUMNS view columns and their descriptions. This view contains a row of column definition information for each column in each base or nested table you have the authority to access. The TABLE_COLUMNS view contains column definition information not contained in the COLUMNS view, for example, the name of the Model 204 field to which the column maps.
The top-to-bottom order of the columns in the following table is the left-to-right order of the columns in each row of output you receive from an unqualified SELECT * query against the view.
| Column name | Data type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| TABLE_CATALOG | CHAR(18) | Name of the catalog in which the table is cataloged (CCACAT) |
| TABLE_SCHEMA | CHAR(18) | Name of the schema to which the table belongs |
| TABLE_NAME | CHAR(18) | Name of the table |
| COLUMN_NAME | CHAR(18) | Name of the column |
| FIELD_NAME | CHAR(255) | Name of the Model 204 field to which the column maps |
| NUMERIC_PRECISION | INTEGER | Maximum numeric precision of the column values |
| NUMERIC_SCALE | INTEGER | Numeric scale of the column values |
| CHAR_MAX_LENGTH | INTEGER | Maximum length of string values, if the column data type is CHAR; otherwise, zero |
| DATA_TYPE | CHAR(10) | SQL data type of the column (not the Model 204 field attribute) |
| NULL_ALLOWED | CHAR(1) | 1, if NULL values are allowed for the column; otherwise, 0 |
| COL_UNIQUE | CHAR(1) | 1, if the values in the column are unique; otherwise, 0 |
COLUMNS view
The following table lists the CATALOG.COLUMNS view columns and their descriptions. The COLUMNS view contains a row of column definition information for each column in each base table, nested table, or view you have the authority to access.
Column information for views is limited to the column name. For more view column attribute information, query the TABLE_COLUMNS view for the base tables referenced in the view definition FROM clause.
The top-to-bottom order of the columns in the following table is the left-to-right order of the columns in each row of output you receive from an unqualified SELECT * query against the view.
| Column name | Data type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| TABLE_CATALOG | CHAR(18) | Name of the catalog in which the column's table is cataloged (CCACAT) |
| TABLE_SCHEMA | CHAR(18) | Name of the schema to which the column's table or view belongs |
| TABLE_NAME | CHAR(18) | Name of the column's table or view |
| COLUMN_NAME | CHAR(18) | Name of the column |
| NUMERIC_PRECISION | INTEGER | Table columns: maximum numeric precision of the table column values View columns: 0 (not stored) |
| NUMERIC_SCALE | INTEGER | Table columns: numeric scale of the column values View columns: 0 (not stored) |
| CHAR_MAX_LENGTH | INTEGER | Table columns: maximum length of string values, if the column data type is CHAR; otherwise, zero View columns: 0 (not stored) |
| DATA_TYPE | CHAR(10) | Table columns: SQL data type of the column (derived for views from the corresponding columns in the underlying base tables) View columns: UNAVAIL (not stored) |
VIEWS view
The following table lists the CATALOG.VIEWS view columns and their descriptions. The VIEWS view contains a row of information including the view definition for each view you have the authority to access.
Except for the view definition, CATALOG.VIEWS does not provide information about tables or columns referenced by views you have the authority to access.
If a view definition has more than 255 characters, it is continued in the VIEW_DEFINITION column on one or more additional rows. Except for the view definition, the column values in these extra rows duplicate those in the row with the beginning of the view definition.
The top-to-bottom order of the columns in the following table is the left-to-right order of the columns in each row of output you receive from an unqualified SELECT * query against the view.
| Column name | Data type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| TABLE_CATALOG | CHAR(18) | Name of the catalog in which the view is cataloged (CCACAT) |
| TABLE_SCHEMA | CHAR(18) | Name of the schema to which the view belongs |
| TABLE_NAME | CHAR(18) | Name of the view |
| VIEW_DEFINITION | CHAR(255) | The view definition source string without the CREATE VIEW viewname phrase. You might want to include TABLE_SCHEMA and TABLE_NAME in your query to help identify the view definition output. |
| CHECK_OPTION | CHAR(1) | 1, if WITH CHECK OPTION clause is present in the view definition; otherwise, 0 |
| UPDATABLE | CHAR(1) | 1, if data may be inserted, deleted, or updated through this view; otherwise, 0 |
TABLE_CONSTRAINTS view
The following table lists the CATALOG.TABLE_CONSTRAINTS view columns and their descriptions. The TABLE_CONSTRAINTS view contains a row of information for each multi-column unique constraint in a base table you have the authority to access.
This view displays only multi-column unique constraints; primary key and foreign key constraints are not displayed. The names of the columns participating in each multi-column unique key are displayed in the KEY_COLUMN_USAGE view.
The top-to-bottom order of the columns in the following table is the left-to-right order of the columns in each row of output you receive from an unqualified SELECT * query against the view.
| Column name | Data type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| CONSTRAINT_CATALOG | CHAR(18) | Name of the catalog in which the constraint table is cataloged (CCACAT) |
| CONSTRAINT_SCHEMA | CHAR(18) | Name of the schema to which the constraint table belongs |
| TABLE_NAME | CHAR(18) | Name of the table in which the constraint was defined |
| CONSTRAINT_FIELD | CHAR(255) | Name of the UNIQUE Model 204 field that is used to generate the Model 204 index and constraints |
| CONSTRAINT_TYPE | CHAR(1) | U, for unique |
| TIMESTAMP | CHAR(14) | Greenwich mean time when the table constraint was cataloged |
KEY_COLUMN_USAGE view
The following table lists the CATALOG.KEY_COLUMN_USAGE view columns and their descriptions. The KEY_COLUMN_USAGE view contains a row of information for each multicolumn unique constraint in each base table you have the authority to access. The information includes the name of each column participating in a multicolumn unique key.
This view is only for columns that participate in multicolumn unique constraints; primary key and foreign key constraints are not displayed.
The top-to-bottom order of the columns in the following table is the left-to-right order of the columns in each row of output you receive from an unqualified SELECT * query against the view.
| Column name | Data type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| CONSTRAINT_CATALOG | CHAR(18) | Name of the catalog in which the constraint table is cataloged (CCACAT) |
| CONSTRAINT_SCHEMA | CHAR(18) | Name of the schema to which the constraint table belongs |
| TABLE_NAME | CHAR(18) | Name of the table in which the constraint is defined |
| CONSTRAINT_FIELD | CHAR(255) | Name of the UNIQUE Model 204 field that is used to generate Model 204 index and constraints |
| COLUMN_NAME | CHAR(18) | Name of a column that participates in a multicolumn constraint; one row is returned for each column used in a multicolumn unique key |
TABLE_PRIVILEGES view
The following table lists the CATALOG.TABLE_PRIVILEGES view columns and their descriptions. The TABLE_PRIVILEGES view contains a row for each table and view for which you have or have granted a DML update privilege.
The top-to-bottom order of the columns in the following table is the left-to-right order of the columns in each row of output you receive from an unqualified SELECT * query against the view.
| Column name | Data type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| GRANTOR | CHAR(18) | Authorization ID of the user giving the privilege |
| GRANTEE | CHAR(18) | Authorization ID, which may be PUBLIC (all users), of the user given the privilege |
| TABLE_CATALOG | CHAR(18) | Name of the catalog in which the table or view is cataloged (CCACAT) |
| TABLE_SCHEMA | CHAR(18) | Name of the schema to which the table or view belongs |
| TABLE_NAME | CHAR(18) | Name of the table or view |
| PRIVILEGE | CHAR(6) | Type of privilege: SELECT, INSERT, DELETE, or UPDATE |
| GRANTABLE | CHAR(1) | 1, if the privilege includes WITH GRANT OPTION; otherwise, 0 |
| TIMESTAMP | CHAR(14) | Greenwich mean time when the table privilege was cataloged |
COLUMN_PRIVILEGES view
The following table lists the CATALOG.COLUMN_PRIVILEGES view columns and their descriptions. The COLUMN_PRIVILEGES view contains a row for each DML update privilege you have or have granted for a column.
The top-to-bottom order of the columns in the following table is the left-to-right order of the columns in each row of output you receive from an unqualified SELECT * query against the view.
| Column name | Data type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| GRANTOR | CHAR(18) | Authorization ID of the user giving the privilege |
| GRANTEE | CHAR(18) | Authorization ID, which may be PUBLIC (all users), of the user given the privilege |
| TABLE_CATALOG | CHAR(18) | Name of the catalog in which the table or view is cataloged (CCACAT) |
| TABLE_SCHEMA | CHAR(18) | Name of the schema to which the table or view belongs |
| TABLE_NAME | CHAR(18) | Name of the table or view |
| COLUMN_NAME | CHAR(18) | Name of a column from the list of columns for which update privilege is granted; one row is returned for each such column |
| PRIVILEGE | CHAR(6) | Type of privilege: SELECT, INSERT, DELETE, or UPDATE |
| GRANTABLE | CHAR(1) | 1, if the privilege includes WITH GRANT OPTION; otherwise, 0 |
| TIMESTAMP | CHAR(14) | Greenwich mean time when the column privilege was cataloged |
ODBC_TYPES view
The following table lists the CATALOG.ODBC_TYPES and their descriptions. The ODBC_TYPES view contains a row of information for each discrete data type supported by the Connect★ drivers.
| Column name | Data type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| TYPE_NAME | CHAR(16) | Name of a data type that can be used for defining columns to be accessed through ODBC |
| DATA_TYPE | CHAR(15) | Data type code number for the data type, as specified in the ODBC API |
| PRECISION_VAL | INTEGER(4) | Maximum precision for this data type. 0 is returned, if precision is not applicable |
| LITERAL_PREFIX | CHAR(1) | Character used to prefix a literal. For example, a single quotation mark (') is used for CHAR data type literals |
| LITERAL_SUFFIX | CHAR(1) | Character used to terminate a literal, for example, a single quotation mark (') is used to terminal a CHAR data type literal |
| CREATE_PARAMS | CHAR(15) | Description of the creation parameters for this data type. For example, LENGTH is specified for a CHAR data type |
| NULLABLE | SMALLINT(2) | Flag indicating whether columns with this data type are nullable 1 indicates yes |
| CASE_SENSITIVE | SMALLINT(2) | 1 means columns of this type are case sensitive 0 means they are not |
| SEARCHABLE | SMALLINT(2) | 2 means columns of this type can be used in a WHERE clause on a SELECT, except with LIKE 3 means they can be used also with LIKE |
| UNSIGNED_ATTRIBUTE | SMALLINT | 1 means the data type is unsigned; 0 means it is signed |
| MONEY | SMALLINT(2) | 1 means a monetary data type; 0 means it is not |
| AUTO_INCREMENT | SMALLINT(2) | 1 means columns of this type are automatically incremented (set to a unique value when a new row is inserted) 0 means they are not automatically incremented |
| LOCAL_TYPE_NAME | CHAR(10) | Localized name for this data type on this data source that is different from the standard data type name |
| RADIX | SMALLINT(2) | Number base used for showing numeric values for this data type; for example, 10 means that decimal values are shown |
| MINIMUM_SCALE | SMALLINT(2) | Minimum scale associated with this data type |
| MAXIMUM_SCALE | SMALLINT(2) | Maximum scale associated with this data type |
ODBC_SCALES view
The following table lists the CATALOG.ODBC_SCALES view columns and their descriptions.
| Column name | Data type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| CHAR_SCALE | CHAR(4) | |
| ODBC_SCALE | SMALLINT(2) |
CONST view
The following table lists the CATALOG.CONST view columns and their descriptions.
| Column name | Data type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| DOUBLE_NULL | DOUBLE PRECISION(8) | |
| INTEGER_NULL | INTEGER(4) | |
| REAL_NULL | REAL(4) | |
| SMALLINT_NULL | SMALLINT(2) | |
| CHAR1_NULL | CHAR(1) | |
| CHAR12_NULL | CHAR(12) | |
| CHAR18_NULL | CHAR(18) | |
| CHAR128_NULL | CHAR(128) | |
| CHAR255_NULL | CHAR(255) |
ODBC_COLUMNS view
The following table lists the CATALOG.ODBC_COLUMNS view columns and their description. The ODBC_COLUMNS view contains a row of information for each discrete column defined to a catalogued table, and describes the type of data that can be held in that column.
| Column name | Data type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| TABLE_QUALIFIER | CHAR(18) | Name of the catalog in which the column's table is catalogued (CCACAT) |
| TABLE_OWNER | CHAR(18) | Name of the owning schema (or ID) to which the column's table belongs |
| TABLE_NAME | CHAR(18) | Name of the table containing the column |
| COLUMN_NAME | CHAR(18) | Name of the column |
| DATA_TYPE | SMALLINT(2) | Integer code for the data type that is defined for this column (as described in the ODBC_TYPES view) |
| TYPE_NAME | CHAR(16) | Name of the data type used for this column |
| PRECISION_VAL | INTEGER(4) | Maximum number of significant digits available for values for this column |
| LENGTH | INTEGER(4) | Length in bytes of the data type used for this column |
| SCALE | CHAR(4) | Number of digits available to the right of the decimal point for values for this column |
| RADIX | SMALLINT(2) | The number base used for numerical values for this column. 10 indicates decimal values. |
| NULLABLE | SMALLINT(2) | 1 means NULLS ALLOWED for this column. 0 means NULLS are not allowed. |
| REMARKS | CHAR(254) | General remarks on the column |
| TABLE_TYPE | CHAR(14) | Either TABLE for a base table, or VIEW, for a view defined against a table |
| SCOPE | SMALLINT(2) | |
| PRIMARY_KEY | CHAR(18) | The primary key for the column's table, if this table is a parent table |
| PARENT_TABLE_NAME | CHAR(18) | The parent table name, if the column's table is a nested table |
| SYSTEM_KEY | CHAR(1) | The name of the system generated key used as a unique identifier, if the column's table is a parent table. |
| NON_UNIQUE | ||
| TYPE_CODE | ||
| SEQ_IN_INDEX |
ODBC_TABLES view
The following table lists the CATALOG.ODBC_TABLES view columns and their descriptions. The ODBC_TABLES view contains a row of information for each discrete catalogued table or view.
| Column name | Data type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| TABLE_QUALIFIER | CHAR(18) | Name of the catalog in which the table is catalogued (CCACAT) |
| TABLE_OWNER | CHAR(18) | Name of the owning schema (or ID) to which the table belongs |
| TABLE_NAME | CHAR(18) | Name of the table or view |
| TABLE_TYPE | CHAR(12) | Either TABLE for base table or VIEW for a view defined against a table |
| REMARKS | CHAR(254) | General notes on the table |
ODBC_SPECIAL_COLS view
The following table lists the CATALOG.ODBC_SPECIAL_COLS view columns and their descriptions. The ODBC_SPECIAL_COLS view contains a row of information for each discrete column that is used to uniquely identify rows within a table. This view may also be used to show other specialized columns in the future.
| Column name | Data type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| TABLE_QUALIFIER | CHAR(18) | Name of the catalog in which the column's table is catalogued (CCACAT) |
| TABLE_OWNER | CHAR(18) | Name of the owning schema (or ID) to which the column's table belongs |
| TABLE_NAME | CHAR(18) | Name of the table containing the specialized column |
| SCOPE | SMALLINT(2) | |
| COLUMN_NAME | CHAR(18) | Name of the specialized column. Typically this will be the name of the primary key of a parent table |
| DATA_TYPE | SMALLINT(2) | Integer code for the data type that is defined for this column (as described in the ODBC_TYPES view). |
| TYPE_NAME | CHAR(16) | Name of the data type used for this column |
| PRECISION_VAL | INTEGER(4) | Maximum number of significant digits available for values for this column |
| LENGTH | INTEGER(4) | Length in bytes of the data type used for this column |
| SCALE | SMALLINT(2) | Number of digits available to the right of the decimal point for values for this column |
ODBC_TABLE_STATS view
The following table lists the CATALOG.ODBC_TABLE_STATS view columns and their descriptions. The ODBC_TABLE_STATS view contains a row of information for each discrete catalogued table or view.
| Column name | Data type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| TABLE_QUALIFIER | CHAR(18) | Name of the catalog in which the table is catalogues (CCACAT) |
| TABLE_OWNER | CHAR(18) | Name of the owning schema (or ID) to which the table belongs |
| TABLE_NAME | CHAR(18) | Name of the table or view |
| NON_UNIQUE | SMALLINT(2) | |
| INDEX_QUALIFIER | CHAR(18) | |
| INDEX_NAME | CHAR(18) | |
| TYPE_CODE | SMALLINT(2) | |
| SEQ_IN_INDEX | SMALLINT(2) | |
| COLUMN_NAME | CHAR(18) | |
| COLLATION | CHAR(1) | |
| CARDINALITY | INTEGER(4) | |
| PAGES | INTEGER(4) |
ODBC_KEY_STATS view
The following table lists the CATALOG.ODBC_KEY_STATS view columns and their descriptions.
| Column name | Data type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| TABLE_QUALIFIER | CHAR(18) | Name of the catalog in which the table is cataloged (CCACAT) |
| TABLE_OWNER | CHAR(18) | Name of the owning schema (or ID) to which the table belongs |
| TABLE_NAME | CHAR(181) | Name of the table |
| NON_UNIQUE | SMALLINT(2) | 1 means there is no unique identifier for row in the table. 0 means there is a unique identifier. |
| INDEX_QUALIFIER | CHAR(18) | |
| INDEX_NAME | CHAR(18) | Name of primary index for the table, if the table is a parent table |
| TYPE_CODE | SMALLINT(2) | Type of index |
| SEQ_IN_INDEX | SMALLINT(2) | |
| COLUMN_NAME | CHAR(18) | Name of column used as primary index for the table |
| COLLATION | CHAR(1) | Collation sequence for rows in the table. A = ascending |
| CARDINALITY | INTEGER(4) | Number of rows in the table, or unique values in the primary index |
| PAGES | INTEGER(4) | Number of pages used to store the index or table. |
ODBC_STATISTICS view
The following table lists the CATALOG.ODBC_STATISTICS view columns and their descriptions. The ODBC_STATISTICS view contains a row of information for each discrete catalogued table or view, and is used to return statistics about the table and its indexes.
| Column name | Data type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| TABLE_QUALIFIER | CHAR(18) | Name of the catalog in which the table is catalogued (CCACAT) |
| TABLE_OWNER | CHAR(18) | Name of the owning schema (or ID) to which the table belongs |
| TABLE_NAME | CHAR(180) | Name of the table or view |
| NON_UNIQUE | SMALLINT(2) | 1 means there is no unique identifier for row in the table or view. 0 means there is a unique identifier. |
| INDEX_QUALIFIER | CHAR(18) | |
| INDEX_NAME | CHAR(18) | Name of primary index for the table, if the table is a parent table |
| TYPE_CODE | SMALLINT(2) | Type of index |
| SEQ_IN_INDEX | SMALLINT(2) | |
| COLUMN_NAME | CHAR(18) | Name of column used as primary index for the table |
| COLLATION | CHAR(1) | Collation sequence for rows in the table. A = ascending |
| CARDINALITY | INTEGER(4) | Number of rows in the table, or unique values in the primary index |
| PAGES | INTEGER(4) | Number of pages used to store the index or table. |
See also
- SQL Server overview
- SQL Server installation
- SQL catalog
- SQL representation of Model 204 data
- SQL Data Definition Language (DDL)
- SQL DDL from the Table Specification Facility
- SQL catalog reporting and querying
- SQL Data Manipulation Language (DML)
- SQL DDL syntax
- SQL reserved words
- SQL DDL mapping of the demonstration database