SNAPCTL parameter: Difference between revisions
m misc formatting |
|||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
<p>At initialization only:</p> | <p>At initialization only:</p> | ||
<table> | <table> | ||
<tr><th>Hex setting</th><th>Bits summed</th></tr> | <tr class="head"><th>Hex setting</th><th>Bits summed</th></tr> | ||
<tr><th><var>X'28' (7.5 and later) </var></th><td>Bits X'08' and X'20'</td></tr> | <tr><th><var>X'28' (7.5 and later) </var></th><td>Bits X'08' and X'20'</td></tr> | ||
<tr><th><var>X'41' (z/VM, pre-7.4) </var></th><td>Bits X'01' and X'40'</td></tr> | <tr><th><var>X'41' (z/VM, pre-7.4) </var></th><td>Bits X'01' and X'40'</td></tr> | ||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
<p>The snap and dump action <var class="product">Model 204</var> takes when a snap is produced</p> | <p> | ||
<p>The table below shows the basic settings of SNAPCTL with their associated actions. The top four actions (X '80' through X '10') are the snap options, and the remainder are the dump options. </p> | The [[Storing diagnostic information (CCASNAP)#Overview|snap]] and dump action <var class="product">Model 204</var> takes when a snap is produced</p> | ||
<p>As explained below the table, any SNAPCTL specification actually results in both a snap action and a dump action, because <var class="product">Model 204</var> adds a default snap or dump action to your specification. </p> | <p> | ||
The table below shows the basic settings of <var>SNAPCTL</var> with their associated actions. The top four actions (X '80' through X '10') are the snap options, and the remainder are the dump options. </p> | |||
<p> | |||
As explained below the table, any <var>SNAPCTL</var> specification actually results in both a snap action and a dump action, because <var class="product">Model 204</var> adds a default snap or dump action to your specification. </p> | |||
<table> | <table> | ||
<caption>Snap and dump settings</caption> | <caption>Snap and dump settings</caption> | ||
<tr><th>Hex</th><th>Dec</th><th>Action</th></tr> | <tr class="head"><th>Hex</th><th>Dec</th><th>Action</th></tr> | ||
<tr>< | <tr><th>Snap settings</th></tr> | ||
<tr><th><var>X'80'</var></th><td>128</td><td>Do not produce a snap </td></tr> | <tr><th><var>X'80'</var></th><td>128</td><td>Do not produce a snap </td></tr> | ||
<tr><th><var>X'40'</var></th><td>64</td><td>Snap whatever the individual message specifies</td></tr> | <tr><th><var>X'40'</var></th><td>64</td><td>Snap whatever the individual message specifies</td></tr> | ||
<tr><th><var>X'20'</var></th><td>32</td><td>Smart snap. See [[#Special settings|Special settings]] for more information.</td></tr> | <tr><th><var>X'20'</var></th><td>32</td><td>Smart snap. See [[#Special settings|Special settings]] for more information.</td></tr> | ||
<tr><th><var>X'10'</var></th><td>16</td><td>Produce a complete formatted snap </td></tr> | <tr><th><var>X'10'</var></th><td>16</td><td>Produce a complete formatted snap </td></tr> | ||
<tr>< | <tr><th>Dump settings</th></tr> | ||
<tr><th><var>X'08'</var></th><td>8</td><td>Do not produce a dump</td></tr> | <tr><th><var>X'08'</var></th><td>8</td><td>Do not produce a dump</td></tr> | ||
<tr><th><var>X'05'</var></th><td>5</td><td>Enable an asynchronous dump. See [[#Special settings|Special settings]] for more information.</td></tr> | <tr><th><var>X'05'</var></th><td>5</td><td>Enable an asynchronous dump. See [[#Special settings|Special settings]] for more information.</td></tr> | ||
<tr><th><var>X'04'</var></th><td>4</td><td>Dump whatever the individual message specifies</td></tr> | <tr><th><var>X'04'</var></th><td>4</td><td>Dump whatever the individual message specifies</td></tr> | ||
<tr><th><var>X'02'</var></th><td>2</td><td>Dump whatever the individual message specifies and spin off SNAPs (z/OS). See [[#Special settings|Special settings]] for more information. </td></tr> | <tr><th><var>X'02'</var></th><td>2</td><td>Dump whatever the individual message specifies and spin off SNAPs (z/OS). See [[#Special settings|Special settings]] for more information. </td></tr> | ||
<tr><th><var>X'01'</var></th><td>1</td><td>Produce a complete region dump</td></tr> | <tr><th><var>X'01'</var></th><td>1</td><td>Produce a complete region dump</td></tr> | ||
<tr><th><var>X'00'</var></th><td>0</td><td>Do not produce a dump. See [[#Special settings|Special settings]] for more information.</td></tr> | <tr><th><var>X'00'</var></th><td>0</td><td>Do not produce a dump. See [[#Special settings|Special settings]] for more information.</td></tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
====SNAP and dump half-bytes==== | ====SNAP and dump half-bytes==== | ||
<p>The above table is divided into the hexadecimal and decimal settings corresponding to the first (left) four bits of the SNAPCTL value byte, the second four bits, and the special case, zero. </p> | <p> | ||
<p>One SNAPCTL byte, divided into a first half-byte and a second half-byte, controls both the snap action and the system dump action. Your specification for SNAPCTL activates <i>both</i> a snap action and an operating system dump action.</p> | The above table is divided into the hexadecimal and decimal settings corresponding to the first (left) four bits of the SNAPCTL value byte, the second four bits, and the special case, zero. </p> | ||
<p>The first SNAPCTL half-byte controls the snap action, and the second half-byte controls the dump action, as shown below. [[File:Snapdump.jpg]]</p> | <p> | ||
One SNAPCTL byte, divided into a first half-byte and a second half-byte, controls both the snap action and the system dump action. Your specification for SNAPCTL activates <i>both</i> a snap action and an operating system dump action.</p> | |||
<p> | |||
The first SNAPCTL half-byte controls the snap action, and the second half-byte controls the dump action, as shown below. [[File:Snapdump.jpg]]</p> | |||
====Including half-byte defaults==== | ====Including half-byte defaults==== | ||
<p>The SNAPCTL default takes effect at initialization. If you set or reset SNAPCTL, <var class="product">Model 204</var> overrides the initialization default and replaces it with separate defaults for each SNAPCTL half-byte. Under Model 204 7.5 and later, X'20' is the snap half-byte default and X'08' is the dump half-byte default. Under earlier Model 204 versions, X'40' is the snap half-byte default and X'04' is the dump half-byte default.</p> | <p> | ||
<p>The default for a half-byte takes effect only if your SNAPCTL setting includes none of the bits of that half-byte. For example, if you specify SNAPCTL=X '08', you are including none of the snap half-byte bits. <var class="product">Model 204</var> sets the X'08' dump action ("no dump") and includes the snap half-byte default action (X'20', "minimal CCASNAP" under Model 204 7.5 and later).</p> | The SNAPCTL default takes effect at initialization. If you set or reset SNAPCTL, <var class="product">Model 204</var> overrides the initialization default and replaces it with separate defaults for each SNAPCTL half-byte. Under Model 204 7.5 and later, X'20' is the snap half-byte default and X'08' is the dump half-byte default. Under earlier Model 204 versions, X'40' is the snap half-byte default and X'04' is the dump half-byte default.</p> | ||
<p> | |||
The default for a half-byte takes effect only if your SNAPCTL setting includes none of the bits of that half-byte. For example, if you specify SNAPCTL=X '08', you are including none of the snap half-byte bits. <var class="product">Model 204</var> sets the X'08' dump action ("no dump") and includes the snap half-byte default action (X'20', "minimal CCASNAP" under Model 204 7.5 and later).</p> | |||
<p>Your specification of X'08' is translated to X'28'. When a snap is called for, <var class="product">Model 204</var> snaps whatever the message specifies and produces no dump. If you VIEW SNAPCTL, <var class="product">Model 204</var> displays: </p> | <p>Your specification of X'08' is translated to X'28'. When a snap is called for, <var class="product">Model 204</var> snaps whatever the message specifies and produces no dump. If you VIEW SNAPCTL, <var class="product">Model 204</var> displays: </p> | ||
<p class="code">SNAPCTL X'28' SNAP/DUMP OPTIONS | <p class="code">SNAPCTL X'28' SNAP/DUMP OPTIONS | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
<p>Similarly, if you specify SNAPCTL=X'20', <var class="product">Model 204</var> sets the X'20' snap action ("smart snap") and includes the dump half-byte default action (X'08', "no dump" under Model 204 7.5 and later). Your specification of X'20' is translated to X'28'. If you VIEW SNAPCTL, <var class="product">Model 204</var> displays: </p> | <p> | ||
Similarly, if you specify SNAPCTL=X'20', <var class="product">Model 204</var> sets the X'20' snap action ("smart snap") and includes the dump half-byte default action (X'08', "no dump" under Model 204 7.5 and later). Your specification of X'20' is translated to X'28'. If you VIEW SNAPCTL, <var class="product">Model 204</var> displays: </p> | |||
<p class="code">SNAPCTL X'28' SNAP/DUMP OPTIONS | <p class="code">SNAPCTL X'28' SNAP/DUMP OPTIONS | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
<p>If you specify a SNAPCTL setting that includes bits from both half-bytes, neither half-byte default action is automatically included. For example, if you specify SNAPCTL=X '41', <var class="product">Model 204</var> combines the X'40' action ("snap whatever the message specifies") and the X '01' action (region dump). If you VIEW SNAPCTL, <var class="product">Model 204</var> displays: </p> | <p> | ||
If you specify a SNAPCTL setting that includes bits from both half-bytes, neither half-byte default action is automatically included. For example, if you specify SNAPCTL=X '41', <var class="product">Model 204</var> combines the X'40' action ("snap whatever the message specifies") and the X '01' action (region dump). If you VIEW SNAPCTL, <var class="product">Model 204</var> displays: </p> | |||
<p class="code">SNAPCTL X'41' SNAP/DUMP OPTIONS | <p class="code">SNAPCTL X'41' SNAP/DUMP OPTIONS | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
<p>You cannot specify a combination of two snap half-byte bits or two dump half-byte bits. With one exception, the bit settings within each half-byte are mutually exclusive. For example, if you specify SNAPCTL=X'60' (X'40' plus X'20'), you get an error message stating that conflicting attributes prevent the resetting of SNAPCTL.</p> | <p> | ||
You cannot specify a combination of two snap half-byte bits or two dump half-byte bits. With one exception, the bit settings within each half-byte are mutually exclusive. For example, if you specify SNAPCTL=X'60' (X'40' plus X'20'), you get an error message stating that conflicting attributes prevent the resetting of SNAPCTL.</p> | |||
<p>X'02' is the only bit setting that you can combine with other bits in its half-byte. For example, if you specify SNAPCTL=X'43', you get the combined actions of X'02', X'01', and X'40'. </p> | <p>X'02' is the only bit setting that you can combine with other bits in its half-byte. For example, if you specify SNAPCTL=X'43', you get the combined actions of X'02', X'01', and X'40'. </p> | ||
====Special settings==== | ====Special settings==== | ||
<p>The following SNAPCTL settings require further comment.</p> | <p> | ||
The following SNAPCTL settings require further comment.</p> | |||
<table> | <table> | ||
<tr><th> | <tr class="head"><th> | ||
<p>SNAPCTL setting</p> | <p>SNAPCTL setting</p> | ||
</th><th> | </th> | ||
<p>Comments...</p> | <th><p>Comments...</p></th></tr> | ||
</th></tr> | |||
<tr><th><var> | <tr><th><var> | ||
<p>X '00'</p> | <p>X '00'</p> | ||
| Line 74: | Line 95: | ||
<p>The zero bit is treated as if it belongs to the dump half-byte. Specifying SNAPCTL=X '00' is equivalent to specifying SNAPCTL=X '08'.</p> | <p>The zero bit is treated as if it belongs to the dump half-byte. Specifying SNAPCTL=X '00' is equivalent to specifying SNAPCTL=X '08'.</p> | ||
</td></tr> | </td></tr> | ||
<tr><th><var> | <tr><th><var> | ||
<p>X'02'</p> | <p>X'02'</p> | ||
</var></th><td> | </var></th> | ||
<p>Under only z/OS, you can spin off a snap. Spinning off a snap means dynamically allocating the snap to SYSOUT, making output available immediately rather than waiting for the end of the run. </p> | <td><p>Under only z/OS, you can spin off a snap. Spinning off a snap means dynamically allocating the snap to SYSOUT, making output available immediately rather than waiting for the end of the run. </p> | ||
</td></tr> | </td></tr> | ||
<tr><th><var> | |||
<p>X'05'</p> | <tr><th><var><p>X'05'</p></var></th> | ||
</var></th><td> | <td><p> | ||
<p>Under only z/OS, you can enable a complete region [[#Asynchronous dump option for z/OS|asynchronous dump]]. <br /> | Under only z/OS, you can enable a complete region [[#Asynchronous dump option for z/OS|asynchronous dump]]. <br /> | ||
This setting is not required when SYSMDUMP or CCAMDMP<i>n</i> DDs are present. If set to 5 in those cases, two SVCDUMPs will be generated: one to DSN=SYS1.DUMP<i>nn</i> and one to //SYSMDUMP or //CCAMDMP<i>n</i>.</p> | This setting is not required when SYSMDUMP or CCAMDMP<i>n</i> DDs are present. If set to 5 in those cases, two SVCDUMPs will be generated: one to DSN=SYS1.DUMP<i>nn</i> and one to //SYSMDUMP or //CCAMDMP<i>n</i>.</p> | ||
</td></tr> | </td></tr> | ||
<tr><th><var> | |||
<p>X'20'</p> | <tr><th><var><p>X'20'</p></var></th> | ||
</var></th><td> | <td><p>If SNAPCTL=X '20', <var class="product">Model 204</var> takes a snap of the registers, module link map, allocated storage map, pushdown list trace, KOMM, areas near registers at the time of the error, disk buffers containing Model 204 file pages held by the current user, the current user's server, patch information, and other contextually determined areas. In general, this is a good setting for snaps as the control blocks necessary to diagnose most problem are likely to be in such a snap whereas any more complete snaps are likely to be massive and unwieldy and not contain any more useful information, anyway. As such, CCASNAPs produced with the X'20 SNAPCTL setting are called <i>smart snaps</i>.</p> | ||
<p>If SNAPCTL=X '20', <var class="product">Model 204</var> takes a snap of the registers, module link map, allocated storage map, pushdown list trace, KOMM, areas near registers at the time of the error, disk buffers containing Model 204 file pages held by the current user, the current user's server, patch information, and other contextually determined areas. In general, this is a good setting for snaps as the control blocks necessary to diagnose most problem are likely to be in such a snap whereas any more complete snaps are likely to be massive and unwieldy and not contain any more useful information, anyway. As such, CCASNAPs produced with the X'20 SNAPCTL setting are called <i>smart snaps</i>.</p> | <p> | ||
<p>See [[SNAPPDLX parameter|SNAPPDLX: PDL SNAP extender]] if you are having Horizon thread problems.</p> | See [[SNAPPDLX parameter|SNAPPDLX: PDL SNAP extender]] if you are having Horizon thread problems.</p> | ||
</td></tr> | </td></tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
====Asynchronous dump option for z/OS==== | ====Asynchronous dump option for z/OS==== | ||
<p>You can generate asynchronous SVC dumps and write to SYS1.DUMP data sets on <var class="product">Model 204</var> ABENDs. <var class="product">Model 204</var> continues as soon as the pages are copied to the DUMPSERV address space. All physical I/O is done from DUMPSERV, which frees the Online system sooner.</p> | <p> | ||
<p>You can enable the asynchronous dump by specifying SNAPCTL=X'05', which is a separate setting that produces a complete region asynchronous dump.</p> | You can generate asynchronous SVC dumps and write to SYS1.DUMP data sets on <var class="product">Model 204</var> ABENDs. <var class="product">Model 204</var> continues as soon as the pages are copied to the DUMPSERV address space. All physical I/O is done from DUMPSERV, which frees the Online system sooner.</p> | ||
<p> | |||
You can enable the asynchronous dump by specifying SNAPCTL=X'05', which is a separate setting that produces a complete region asynchronous dump.</p> | |||
<p><b>WARNING:</b> Familiarize yourself with the memory requirements of the asynchronous dump process to ensure that enough expanded and page space is available. Memory shortage can cause severe system degradation while an asynchronous dump is processing the DUMPSERV address space. <b>If you use this setting and you have not properly configured the DUMPSERV memory requirements, you risk locking your z/OS system.</b></p> | <p class="warn"><b>WARNING:</b> Familiarize yourself with the memory requirements of the asynchronous dump process to ensure that enough expanded and page space is available. Memory shortage can cause severe system degradation while an asynchronous dump is processing the DUMPSERV address space. <b>If you use this setting and you have not properly configured the DUMPSERV memory requirements, you risk locking your z/OS system.</b></p> | ||
<p>If the dump is not taken, due to suppression by SLIP traps-Dump Analysis Elimination (DAE) or a z/OS problem, the following IBM error message is written to the operator:</p> | <p> | ||
If the dump is not taken, due to suppression by SLIP traps-Dump Analysis Elimination (DAE) or a z/OS problem, the following IBM error message is written to the operator:</p> | |||
<p class="code">MODEL 204 SDUMPX FAILED - REASON <i>nn</i></p> | <p class="code">MODEL 204 SDUMPX FAILED - REASON <i>nn</i></p> | ||
<p>The reason codes are listed in the SDUMPX macro in the z/OS Auth Assm Service Reference LLA-SDU. The number of the manual varies according to the release of z/OS.</p> | <p> | ||
The reason codes are listed in the SDUMPX macro in the z/OS Auth Assm Service Reference LLA-SDU. The number of the manual varies according to the release of z/OS.</p> | |||
====Comparing SNAPCTL to MSGCTL==== | ====Comparing SNAPCTL to MSGCTL==== | ||
<p>The SNAPCTL parameter settings correspond to the following MSGCTL command options: </p> | <p> | ||
The SNAPCTL parameter settings correspond to the following MSGCTL command options: </p> | |||
<table> | <table> | ||
<tr><th>SNAPCTL setting</th><th>MSGCTL option</th></tr> | <tr><th>SNAPCTL setting</th><th>MSGCTL option</th></tr> | ||
| Line 111: | Line 139: | ||
<tr><th align="right"><var>128 </var></th><td>NOSNAP</td></tr> | <tr><th align="right"><var>128 </var></th><td>NOSNAP</td></tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
[[Category:System parameters]] | [[Category:System parameters]] | ||
[[Category:Parameters]] | [[Category:Parameters]] | ||
Revision as of 01:12, 9 March 2017
Snap/dump options
Summary
- Default value
-
At initialization only:
Hex setting Bits summed X'28' (7.5 and later) Bits X'08' and X'20' X'41' (z/VM, pre-7.4) Bits X'01' and X'40' X'44' (z/OS, z/VSE, pre7.5) Bits X'04' and X'40' - Parameter type
- System
- Where set
- On User 0's parameter line or reset by system manager
- Related products
- All
- Introduced
- Model 204 V6.1 or earlier
Description
The snap and dump action Model 204 takes when a snap is produced
The table below shows the basic settings of SNAPCTL with their associated actions. The top four actions (X '80' through X '10') are the snap options, and the remainder are the dump options.
As explained below the table, any SNAPCTL specification actually results in both a snap action and a dump action, because Model 204 adds a default snap or dump action to your specification.
| Hex | Dec | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Snap settings | ||
| X'80' | 128 | Do not produce a snap |
| X'40' | 64 | Snap whatever the individual message specifies |
| X'20' | 32 | Smart snap. See Special settings for more information. |
| X'10' | 16 | Produce a complete formatted snap |
| Dump settings | ||
| X'08' | 8 | Do not produce a dump |
| X'05' | 5 | Enable an asynchronous dump. See Special settings for more information. |
| X'04' | 4 | Dump whatever the individual message specifies |
| X'02' | 2 | Dump whatever the individual message specifies and spin off SNAPs (z/OS). See Special settings for more information. |
| X'01' | 1 | Produce a complete region dump |
| X'00' | 0 | Do not produce a dump. See Special settings for more information. |
SNAP and dump half-bytes
The above table is divided into the hexadecimal and decimal settings corresponding to the first (left) four bits of the SNAPCTL value byte, the second four bits, and the special case, zero.
One SNAPCTL byte, divided into a first half-byte and a second half-byte, controls both the snap action and the system dump action. Your specification for SNAPCTL activates both a snap action and an operating system dump action.
The first SNAPCTL half-byte controls the snap action, and the second half-byte controls the dump action, as shown below. 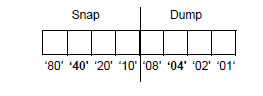
Including half-byte defaults
The SNAPCTL default takes effect at initialization. If you set or reset SNAPCTL, Model 204 overrides the initialization default and replaces it with separate defaults for each SNAPCTL half-byte. Under Model 204 7.5 and later, X'20' is the snap half-byte default and X'08' is the dump half-byte default. Under earlier Model 204 versions, X'40' is the snap half-byte default and X'04' is the dump half-byte default.
The default for a half-byte takes effect only if your SNAPCTL setting includes none of the bits of that half-byte. For example, if you specify SNAPCTL=X '08', you are including none of the snap half-byte bits. Model 204 sets the X'08' dump action ("no dump") and includes the snap half-byte default action (X'20', "minimal CCASNAP" under Model 204 7.5 and later).
Your specification of X'08' is translated to X'28'. When a snap is called for, Model 204 snaps whatever the message specifies and produces no dump. If you VIEW SNAPCTL, Model 204 displays:
SNAPCTL X'28' SNAP/DUMP OPTIONS
Similarly, if you specify SNAPCTL=X'20', Model 204 sets the X'20' snap action ("smart snap") and includes the dump half-byte default action (X'08', "no dump" under Model 204 7.5 and later). Your specification of X'20' is translated to X'28'. If you VIEW SNAPCTL, Model 204 displays:
SNAPCTL X'28' SNAP/DUMP OPTIONS
If you specify a SNAPCTL setting that includes bits from both half-bytes, neither half-byte default action is automatically included. For example, if you specify SNAPCTL=X '41', Model 204 combines the X'40' action ("snap whatever the message specifies") and the X '01' action (region dump). If you VIEW SNAPCTL, Model 204 displays:
SNAPCTL X'41' SNAP/DUMP OPTIONS
You cannot specify a combination of two snap half-byte bits or two dump half-byte bits. With one exception, the bit settings within each half-byte are mutually exclusive. For example, if you specify SNAPCTL=X'60' (X'40' plus X'20'), you get an error message stating that conflicting attributes prevent the resetting of SNAPCTL.
X'02' is the only bit setting that you can combine with other bits in its half-byte. For example, if you specify SNAPCTL=X'43', you get the combined actions of X'02', X'01', and X'40'.
Special settings
The following SNAPCTL settings require further comment.
|
SNAPCTL setting |
Comments... |
|---|---|
|
X '00' |
The zero bit is treated as if it belongs to the dump half-byte. Specifying SNAPCTL=X '00' is equivalent to specifying SNAPCTL=X '08'. |
|
X'02' |
Under only z/OS, you can spin off a snap. Spinning off a snap means dynamically allocating the snap to SYSOUT, making output available immediately rather than waiting for the end of the run. |
X'05' |
Under only z/OS, you can enable a complete region asynchronous dump. |
X'20' |
If SNAPCTL=X '20', Model 204 takes a snap of the registers, module link map, allocated storage map, pushdown list trace, KOMM, areas near registers at the time of the error, disk buffers containing Model 204 file pages held by the current user, the current user's server, patch information, and other contextually determined areas. In general, this is a good setting for snaps as the control blocks necessary to diagnose most problem are likely to be in such a snap whereas any more complete snaps are likely to be massive and unwieldy and not contain any more useful information, anyway. As such, CCASNAPs produced with the X'20 SNAPCTL setting are called smart snaps. See SNAPPDLX: PDL SNAP extender if you are having Horizon thread problems. |
Asynchronous dump option for z/OS
You can generate asynchronous SVC dumps and write to SYS1.DUMP data sets on Model 204 ABENDs. Model 204 continues as soon as the pages are copied to the DUMPSERV address space. All physical I/O is done from DUMPSERV, which frees the Online system sooner.
You can enable the asynchronous dump by specifying SNAPCTL=X'05', which is a separate setting that produces a complete region asynchronous dump.
WARNING: Familiarize yourself with the memory requirements of the asynchronous dump process to ensure that enough expanded and page space is available. Memory shortage can cause severe system degradation while an asynchronous dump is processing the DUMPSERV address space. If you use this setting and you have not properly configured the DUMPSERV memory requirements, you risk locking your z/OS system.
If the dump is not taken, due to suppression by SLIP traps-Dump Analysis Elimination (DAE) or a z/OS problem, the following IBM error message is written to the operator:
MODEL 204 SDUMPX FAILED - REASON nn
The reason codes are listed in the SDUMPX macro in the z/OS Auth Assm Service Reference LLA-SDU. The number of the manual varies according to the release of z/OS.
Comparing SNAPCTL to MSGCTL
The SNAPCTL parameter settings correspond to the following MSGCTL command options:
| SNAPCTL setting | MSGCTL option |
|---|---|
| 1 | DUMPALL |
| 8 | NODUMP |
| 16 | SNAPALL |
| 32 | SNAPPDL |
| 128 | NOSNAP |