Table B (File architecture): Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
::[[File:Table B Structure (File Architecture).jpg]] | ::[[File:Table B Structure (File Architecture).jpg]] | ||
Not shown is a 4 byte 'Reuse Queue Page Number' for Unordered Files. If it is present, it is in the lower left hand corner (before the first record on the page). | Not shown is a 4 byte 'Reuse Queue Page Number' for Unordered Files. If it is present, it is in the lower left hand corner ('before' (working backwards) the first record on the page). | ||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
=== Space Management === | === Space Management === | ||
== <div id="Table B (File Architecture) Segments">Table B Segments</div> == | == <div id="Table B (File Architecture) Segments">Table B Segments</div> == | ||
Revision as of 23:47, 10 April 2013
This topic covers the internal architecture of a Model 204 Table B page.
For a discussion of the ways a File Manager may organize these pages in a file, please refer to File Design (File Management).
At a minimum, Table B contains all of the base records in a Model 204 file. If Table X is not enabled it also contains all extension records. If Table E is not enabled, then any data whose contents is greater than 255 bytes must be held as a series of repeating fields.
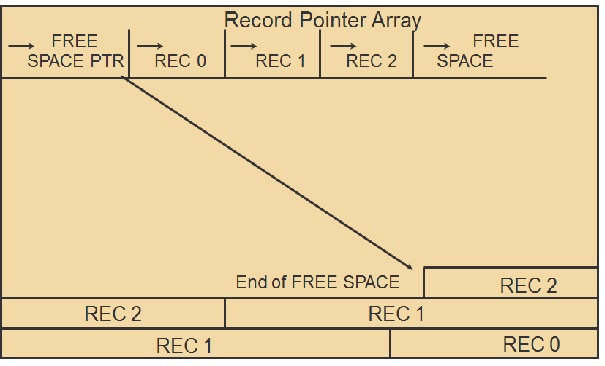
The structure of a Table B page
Not shown is a 4 byte 'Reuse Queue Page Number' for Unordered Files. If it is present, it is in the lower left hand corner ('before' (working backwards) the first record on the page).
Each of the items in the chart are described, below:
Pointers
Free Space Pointer
The free space pointer contains the location of the first byte of free space on the page (as shown in the diagram, where the last record on the page ends). On pages with no records yet stored, it points to the last byte on the page (either the very end, of just before the Reuse Queue Page Number described above).
Record Pointer Array
There are up to BRECPPG record pointers.
Space Management
Table B Segments
Definition
As discussed below, bit maps are used