RKTools: Difference between revisions
m add links |
m mention M204PROC |
||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
All of the <var class="product">RKTools</var> products are <var class="product">Model 204</var> application subsystems written in <var class="product">SOUL</var>. | All of the <var class="product">RKTools</var> products are <var class="product">Model 204</var> application subsystems written in <var class="product">SOUL</var>. | ||
<var class="product">RKTools</var> is distributed as a set of <var class="product">Model 204</var> files in a backup format produced by the <var class="product">Model 204</var> <var>[[DUMP command|DUMP]]</var> command. | <var class="product">RKTools</var> is distributed as a set of <var class="product">Model 204</var> files in a backup format produced by the <var class="product">Model 204</var> <var>[[DUMP command|DUMP]]</var> command. | ||
All <var class="product">SOUL</var>-based products are | All <var class="product">SOUL</var>-based products are | ||
distributed in a single <var class="product">Model 204</var> procedure file | distributed in a single <var class="product">Model 204</var> procedure file. The file is <code>M204PROC</code> as of RKTools 7.7; for earlier versions the file is <code>SIRIUS</code>. | ||
<var class="product">RKTools</var> makes extensive use of specialized [[Object oriented programming in SOUL|SOUL OO]] classes and $functions. These classes and $functions enable the creation of powerful <var class="product">SOUL</var> application systems that can support complex environments with minimal server size requirements. | <var class="product">RKTools</var> makes extensive use of specialized [[Object oriented programming in SOUL|SOUL OO]] classes and $functions. These classes and $functions enable the creation of powerful <var class="product">SOUL</var> application systems that can support complex environments with minimal server size requirements. | ||
| Line 53: | Line 54: | ||
Installing <var class="product">RKTools</var> requires: | Installing <var class="product">RKTools</var> requires: | ||
<ol> | <ol> | ||
<li>Downloading the <code>SIRIUS</code> file and restoring it to the <var class="product">Model 204</var> environment where the tools will run. </li> | <li>Downloading the <code>M204PROC</code> or <code>SIRIUS</code> file, and restoring it to the <var class="product">Model 204</var> environment where the tools will run. </li> | ||
<li>Setting up some subsidiary <var class="product">Model 204</var> files.</li> | <li>Setting up some subsidiary <var class="product">Model 204</var> files.</li> | ||
| Line 62: | Line 63: | ||
For details, see [[RKTools installation]]. | For details, see [[RKTools installation]]. | ||
Upgrades to <var class="product">RKTools</var> can almost always be handled by restoring a fresh copy of the <code>SIRIUS</code> file. | Upgrades to <var class="product">RKTools</var> can almost always be handled by restoring a fresh copy of the <code>M204PROC</code> or <code>SIRIUS</code> file. | ||
==Integrating <var class="product">RKTools</var> with other subsystems== | ==Integrating <var class="product">RKTools</var> with other subsystems== | ||
Revision as of 17:09, 18 May 2017
RKTools — Rocket Tools for Model 204 — is a family of products implemented as SOUL application subsystems, designed to function together in a Model 204 Online. Prior to version 7.5 of RKTools (October, 2015), the product was known as UL/SPF.
Each product in the family can be installed and run independently, or each can be installed and run as a component of the integrated RKTools framework. All RKTools products share a common look and feel, providing a highly productive full screen 3270 interface to a variety of common Model 204 functions. In addition, many of the component subsystems also support web interfaces.
RKTools components
RKTools comprises the following products:
- SirDBA
- A system that analyzes Model 204 databases to determine their logical structure, populating an internal catalog. SirDBA is distributed as a component of the Sir2000 Database Analysis Tools.
- SirFile
- A comprehensive facility both for monitoring the physical storage utilization of Model 204 database files and for warning users of the need for file reorganizations. SirFile maintains historical information that allows it to predict when file sizing problems will occur, allowing a DBA to take preventative action before an application outage results.
- SirLib
- A powerful and flexible system that provides change management and configuration control for Model 204 SOUL applications. SirLib is fully integrated within the SirPro programming environment.
- SirMon
- A comprehensive facility for monitoring the performance and availability of Model 204 online systems. SirMon combines the real time monitoring of Model 204 performance with intelligent full screen displays that facilitate System Manager and Administrator duties.
- SirPro
- A collection of powerful and easy to use tools for programmers, database administrators, and application managers. SirPro provides programmers with powerful facilities for managing large libraries of User Language procedures, and it provides system managers with intuitive ISPF-like front ends to many Model 204 system management commands. As of RKTools Version 7.5, SirPro also incorporates the user-extensible SoulEdit editor, which can also be invoked from the command line via the (optional) Model 204 apsy SE. Because the procedure list feature of SirPro is so central, it too has an optional standalone apsy called PL.
- SirScan
- A high performance utility that allows users in a Model 204 Online to browse the contents of its journal in real time. SirScan permits ordinary users to view journal entries generated by their own online session, and it allows users in ADMIN SCLASSes to browse journal entries for any set of users. The data is displayed in a full-screen browser with powerful searching commands and filtering options.
In addition:
- A number of subsystems that are not linked into the RKTools menuing
structure may be accessed via APSY-transfer from the RKTools applications. One such subsystem is
FACT, a utility for browsing SirFact dumps. - Many sample web and client-server applications developed for the Janus product family are distributed and installed along with the RKTools products. These
include:
JanCat, an application that builds normalized views of Model 204 data for use by Janus Specialty Data Store applications.JanSSL, a Janus Network Security system for creating and managing SSL certificate requests.
- As of version 7.7, RKTools products are accessed by a web interface (RKWeb) as well as by the traditional 3270 interface.
- As of version 7.7, RKTools provides access to Dictionary/204, notably including the Subsystem Management facility (SUBSYSMGMT) and the File Management facility (FILEMGMT).
RKTools packaging and installation requirements
All of the RKTools products are Model 204 application subsystems written in SOUL. RKTools is distributed as a set of Model 204 files in a backup format produced by the Model 204 DUMP command.
All SOUL-based products are
distributed in a single Model 204 procedure file. The file is M204PROC as of RKTools 7.7; for earlier versions the file is SIRIUS.
RKTools makes extensive use of specialized SOUL OO classes and $functions. These classes and $functions enable the creation of powerful SOUL application systems that can support complex environments with minimal server size requirements.
Installing RKTools requires:
- Downloading the
M204PROCorSIRIUSfile, and restoring it to the Model 204 environment where the tools will run. - Setting up some subsidiary Model 204 files.
- Verifying that the environment has the appropriate parameter settings.
For details, see RKTools installation.
Upgrades to RKTools can almost always be handled by restoring a fresh copy of the M204PROC or SIRIUS file.
Integrating RKTools with other subsystems
RKTools and any of its constituent products can be easily integrated with other SOUL subsystems. Whenever an RKTools component product is exiting, it first checks to see if the global variable SIRIUS.COMM exists and has a non-null value. If so, the RKTools product performs a subsystem transfer using the value in SIRIUS.COMM as the name of the target subsystem.
For example, the following code fragment lets you transfer into subsystem SIRMON. When SIRMON exits, control is transferred to the application subsystem MENUSYS, provided that NEXT is the current subsystem's communication global variable:
%rc = $Setg('SIRIUS.COMM','MENUSYS') %rc = $Setg('NEXT','XFER') %rc = $Setg('XFER','SIRMON') STOP
In addition to the individual SOUL subsystems that implement the RKTools products,
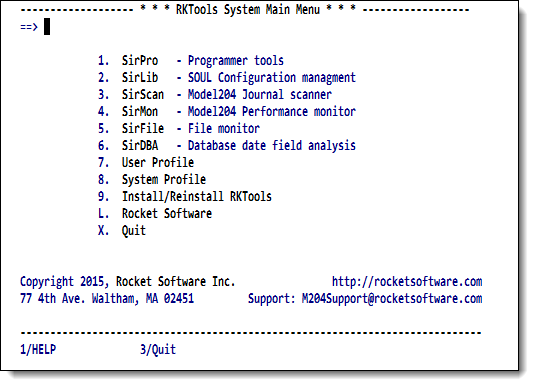
Rocket Software distributes an umbrella RKTools subsystem, accessed by entering RKTOOLS from the Model 204 command line. The RKTOOLS subsystem provides a menu that contains entries for all RKTOOLS components installed at a site:
RKTools main menu
Fast-pathing
The RKTOOLS subsystems support fast-path navigation. For example, a SirMon user can transfer into the SirPro main menu option 1 destination (the SirPro procedure-list selection screen) by using the component subsystem name or short-code along with a menu number:
sirpro 1
Or:
pro 1
And a user in SirScan can enter sirmon 3.1 on the command line and be transferred directly to the option 1 (Resource Usage) destination of the SirMon main menu option 3 (User Monitor) screen.
PL command
PL is both a special subsystem and a command that lets you directly enter the Procedure List screen in SirPro. The command is like a pro 1 fast-path command combined with procedure-search specifications.
The command format is:
PL [procedurePattern] [FILE filename | GROUP groupname]
where procedurePattern supports the wildcard usage described in Procedure name.
If you do not specify a FILE or GROUP clause, one of the following is used:
- The current open context. This context is obtained using
VIEW APDFCNTXor$view('APDFCNTX')(see the APDFCNTX parameter). - The last-visited SirPro procedure list.
Note: To search for procedure names that contain the words "FILE" or "GROUP", use a PL command like the following:
PL File FILE filename
where:
Fileindicates procedures whose name contains the word "File".FILEis required because the context is not automatically added if searching for the words "FILE" or "GROUP".
Release notes
Each RKTools release has the version number of the Model 204 release whose features it can exploit.
For information about member product changes and new features contained in a release, see the RKTools release notes for your version of Model 204 (for example, Release notes for RKTools V7.5).